Overview
Database structure
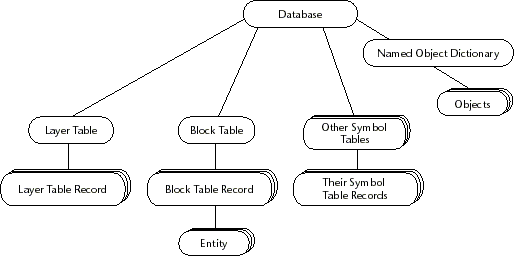
DWG file is a database structure, all graphic information is stored in the database, after mastering the operation of the database will be able to better grasp the control development. Among them, the graph database contains the information of DWG drawings, such as symbol table (block table, layer table, text style sheet, line table, point style sheet), dictionary, pixel object coordinates and other data. The structure of the database is as follows:
Basic object
DWG database stores the objects and entities that constitute graphs. Graphs are collections of objects stored in the database. Basic database objects include entities, symbol tables and dictionaries.
Entity is a specified type of database object, the entity can be a line, circle, arc, text, curve and ellipse. The user can see the entity on the screen and can manipulate it.
Symbol tables and dictionaries are container objects used to store database objects, both of which can map a symbol name to a database object. The database consists of a fixed number of symbol tables, each containing an instance of a particular class as a symbol table record. Examples of the symbol table as data layer surface table (McDbLayerTable(), Layer contains table record) and watch (McDbBlockTable(), which contains block table records), all entities belong to block table records.
Dictionaries provide a more general container object for storing objects than symbol tables, A dictionary can contain any [McDbObject] (https://www.mxdraw3d.com/mxcad_docs/api/classes/2d.McDbObject.html#class-mcdbobject) or other subclass object.
Handle and object ID
During a single use of controls, multiple databases can be loaded, each of which has its own handle and object ID. Handle and ID can uniquely represent an object, the handle can be saved to the graph, the next open drawing will not change, ID is just the current memory address, it is faster than the handle to find the object, but it is not saved with the graph, the next open drawing will change.
With the object ID, the user can obtain a real database object, so that the user can perform related operations on the object.